
Profitability analysis with SAP S/4HANA Finance provides answers to the most important questions for high-level management. SAP S/4HANA is the best solution for a CFO’s entire profitability analysis needs. In this article, our experts at VC ERP answer how!
While SAP COPA is a Controlling module component, it has a close relationship with Finance data. Its combined use cases with finance modules make it an essential part of the S/4HANA Finance conversations.
If we look at the basic structure of any income statement, we can see that Sales Revenue minus Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) equals Gross Profit, which we then deduct Operating Expenses from.
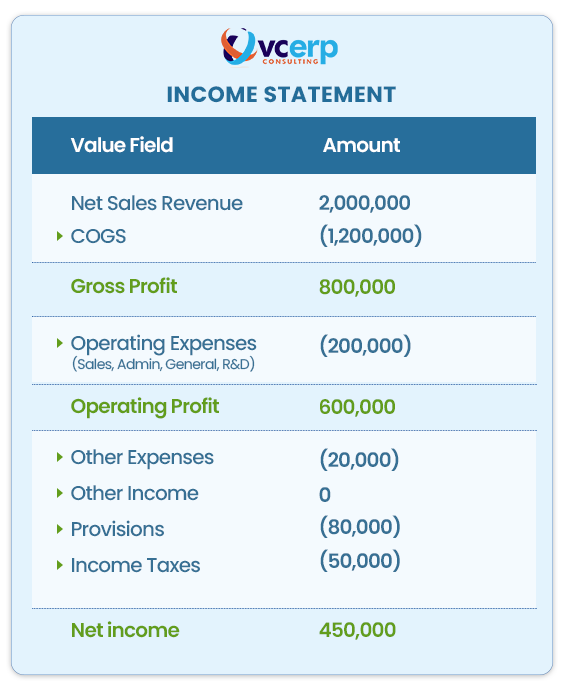
These expenses include general and administrative expenses, as well as research and development (R&D); by removing these expenses, we can derive operational profit. After deducting the provisions, income tax and other income from the income statement, we arrive at the net profit or net income figure.
The income statement contains three significant numbers: gross profit, operational profit and net income. Why are they important?
These metrics will determine whether or not the company is profitable. Is the company making or losing money?
But the revenue statement does not explain the “why” behind these numbers. This is where Profitability Analysis (PA) comes into play.
Why Does Profitability Analysis Matter?
The income statement will not help us comprehend our profitable products or customers. Profitability analysis (PA) will help us understand, for example, why our gross profit is $800,000 in one period but not in another. PA enables us to determine which items and consumers contribute the most to your most profitable categories.
When we look at these data, the gross profit is the easiest to examine because it is directly related to sales. How? Gross profit is the difference between net sales revenue and the cost of items sold. Every unit sold contributes directly to both figures, making the relationship between product and profit clear.
However, when we look at operational profit or net income, for example, these metrics are not directly tied to our sales since they include non-sales expenses such as general and administrative costs. In addition, these expenses cannot be directly attributed to specific items or customers.
All we can do is use certain allocation bases to allocate these products and allocate these expenses as best we can. However, this makes the relationship between expenses and profitability less clear-cut.
Unmasking Indirect Expenses With SAP CO-PA
In short, as a CFO, you want to improve expense attribution and cost tracking. This is where SAP Profitability Analysis addresses your reporting requirements for measuring profitability at the multi-dimensional level.
But, First, What Exactly Is SAP Profitability Analysis?
SAP CO-PA is a powerful tool that helps you map contribution margins and generate short-term profit and loss statements. When we talk about profitability analysis, it involves various methods for measuring a business’s profitability.
Every business organization has two perspectives on profit: external and internal. CFOs often face challenges in gaining internal insights into business performance.
No more!
In fact, SAP S/4HANA COPA provides an internal view of profitability. SAP Profitability Analysis helps users in sales, marketing and product management understand internal profitability.
CO-PA functions similarly to a chef, obtaining all of their ingredients (data) from other kitchens (SAP modules such as Sales, Costing and Production). It rarely cooks anything itself, but rather takes those ingredients and combines them in various ways so as to show how profitable things are.
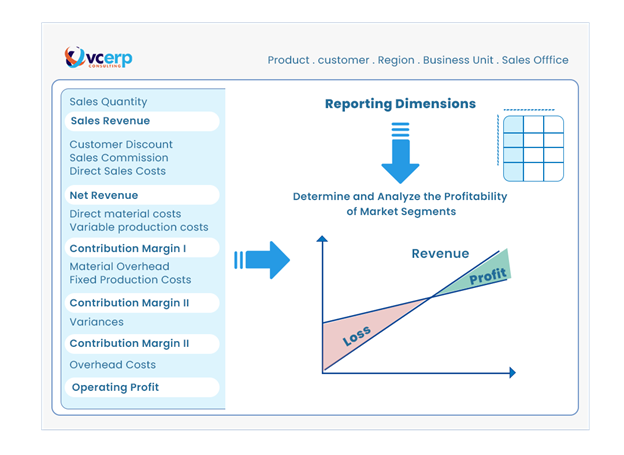
Let’s illustrate this with a scenario: we sell five products to ten consumers in two countries. During a sale, we construct a sales order including product specifications, customer information and shipping destinations. These dimensions are referred to as “characteristics”.
What are “Characteristics” and “Profitability Segment” in SAP COPA?
In SAP S/4HANA, a characteristic can be customers, products, regions, sales branches or any other significant market dimension on which we want to measure our profitability. This is where SAP S/4HANA Profitability Analysis’s power and flexibility lie: its multidimensionality.
When combining the various characteristics, it constitutes a multidimensional “profitability segment”. So, for example, you can ask what my profitability is for customer A with product number 1001 in the country UAE.
The SAP S/4HANA ERP system provides two types of Profitability Analysis: costing-based and account-based.
What Are the Two Types of Profitability Analysis in SAP S/4HANA?
VC ERP’s SAP S/4HANA subject matter experts illustrate the various types of Profitability Analysis in SAP using the example of a manufacturing company.
Consider yourself the CFO of Acme Widgets, a company that manufactures and sells gadgets. You want to know where your profits come from and how different factors influence them.
While SAP recommends using the Margin Analysis evaluation of Controlling Profitability Analysis (COPA), we will discuss both types of PA that exist:
1. Costing-based Profitability Analysis:
Cost-based COPA allows for quick profit analysis for sales management purposes. This type is a detailed breakdown of your production expenses. You can create custom categories (value fields) such as “material cost,” “labour cost” and “overhead cost” and track how much each contributes to the overall cost of making a product.
You may also allocate gadgets to different segments based on variables such as client, product line, or area to determine how profitable each segment is.
Here is an example of a costing-based Profitability Analysis report for Acme Widgets.
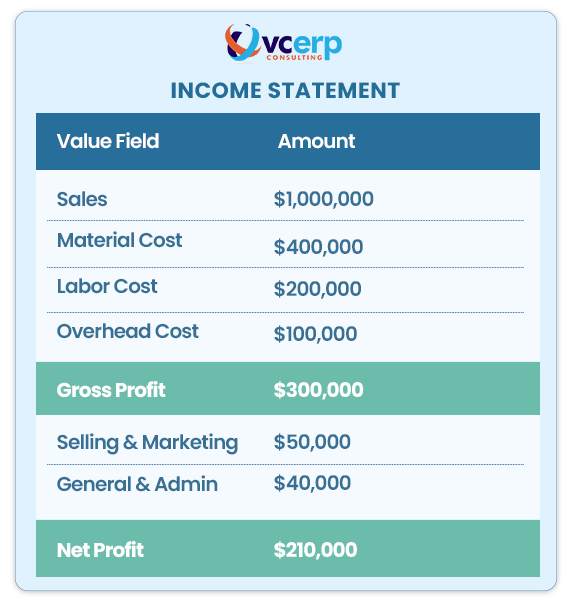
According to this report, Acme Widgets generates a $300,000 gross profit for every $1 million in sales. However, after accounting for sales and administrative costs, the net profit is $210,000.
You can even dive down into certain areas to evaluate how they perform, such as determining whether gadgets sold in the Western region are more profitable than those sold in the Eastern region.
In essence, Costing-Based Profitability Analysis (CO-PA) in SAP–
- Utilizes costing-based values, independent of General Ledger (G/L) accounts, for detailed profitability analysis.
- Defined by characteristics (e.g., customer, gadgets) and value fields (e.g., sales, materials cost).
- Follows Cost of Sales Accounting concept i.e. instead of tracking expenses by type (material, labour, etc.), you group them by department (production, administration, sales & marketing).
- Thus requires reconciliations due to decoupled sales postings and goods issue postings.
- Granular cost and revenue analysis based on various dimensions
- However has complex configuration and customization and limited functionality compared to Account-Based COPA in SAP S/4HANA.
2. Account-Based Profitability Analysis:
Accounts-based COPA allows you to easily reconcile cost and financial accounting using G/L accounts.
Consider the account-based PA (or Margin Analysis) a simplified snapshot of your profitability based on General Ledger (G/L) accounts. Instead of creating custom value fields, you use conventional G/L accounts such as “Sales,” “Cost of Goods Sold” and “Marketing Expense.” This makes it easy to reconcile your Profitability Analysis data with your financial accounting data.
This is an example of an account-based Profitability Analysis report for Acme Widgets.
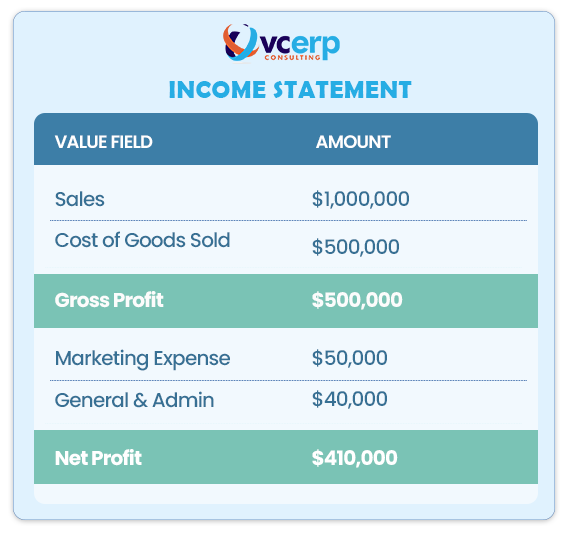
This report provides a slightly different image from the cost-based report.
The COGS is higher, hence the gross profit is also higher. This is because account-based Profitability Analysis normally utilizes a gadget’s standard cost, whereas costing-based Profitability Analysis can track actual manufacturing costs, which may differ.
Confused? Let me break it down!
- Costing-based analysis: Uses actual production costs–which can vary due to over/underconsumption of materials, labor, or overhead.
- Account-based analysis: Often uses standard costs, which are pre-determined averages. This simplifies reconciliations with financial accounting.
Key features of Account-based PA
Account-Based Profitability Analysis (Margin Analysis) provides enhanced functionalities in SAP S/4HANA and here’s a rundown:
- You can split COGS into individual cost components like materials, labour and overheads so that you can analyze their contribution to profitability
- You gain the capability of variance analysis by category (like price discrepancies, quantity deviations, or efficiency losses) so as to pinpoint reasons for cost overruns or savings
- You can build a P&L statement with contribution margin calculation as there is no need for manual data transfer or reconciliation with financial accounting
- You can calculate contribution margin by product, customer, or any relevant segment.
- You can analyze profitability based on up-to-date information
Here’s an illustration to showcase the same-
Cost-based vs Account-based Profitability Analysis in SAP S/4HANA: Comparison
Here’s an overview of the differences between the two types of profitability analysis in SAP S/4HANA.1. Standard vs. Actual Costs:
Account-based profitability typically uses standard costs for materials, labour and overhead. These are predetermined based on average or expected rates, making analysis and reconciliation with financial statements easier. Costing-based profitability can track actual costs, which can differ from standard costs based on production variances and fluctuations.
2. No Custom Value Fields:
Account-based analysis doesn’t utilize custom value fields like in costing-based. All costs are categorized into standard G/L accounts offering a simplified view but potentially less detail on specific cost components.
3. Serve different purposes:
Costing-based offers a fine-grained analysis of production costs with custom categories, useful for optimizing production efficiency and understanding cost variances. While account-based provides a simpler reconciled view of profitability aligning with financial statements. This is convenient for overall financial performance analysis and reporting.
The best approach depends on Acme Widgets’ specific cost analysis and financial reporting requirements.
In SAP S/4HANA, both account-based and costing-based CO-PA are available, but account-based is recommended and most new implementations will use it.
If your company is looking for answers to its profitability analysis reporting requirements, VC ERP FICO consultants can assist you with criteria for activating cost-based Profitability Analysis.
Read more: How SAP S/4HANA Finance Makes Real Time Financial Close PossibleHow SAP S/4HANA Profitability Analysis Helps You See Where Your Money Goes?
As a CFO, you spend your days navigating the complexities of profitability. It’s not a matter of just tracking numbers, it’s about tracking the lifeblood of your business.
Read more: How to scale your Business Flexibily using SAP S/4 HANAWe understand that you need real-time and all-encompassing data on where the money of the enterprise is going and SAP S/4HANA’s Profitability Analysis (CO-PA) is possibly your best weapon.
So, experienced SAP S/4HANA implementation partners like VC ERP consultants are here to explain how SAP S/4HANA will help you track your profits from order to receipt and beyond.
Here’s some food for thought in terms of SAP S/4HANA for profitability analysis. Every step your product takes, from beginning with raw materials to customer invoicing contributes to detailed profitability analysis.
CO-PA fits smoothly with supply chain processes by taking data from manufacturing, shipping and billing. Do you know what it means? No more relying on siloed information or estimated numbers. You get a clear picture of how each transaction and each sales order, impacts your bottom line.
SAP S/4HANA’s margin analysis brings together financial and managerial accounting. It delivers both – consistent financial information without the need for reconciliation as well as a financial audit trail.
Let’s go over some of the key features in detail.
CO-PA’s Data-Driven Decision Engine in SAP S/4HANA
Here’s an overview of the key features and capabilities of SAP S/4HANA COPA.
1. Real time Profitability Insights:
Do not wait for invoices to materialize. CO-PA can show you the potential impact of sales orders before they are shipped or billed. This gives you the ability to change prices, adjust discounts or optimize production in real-time.
Yes, the Gross Margin – Presumed/Actual function in the SAP S/4HANA system allows you to examine profitability using both the expected and actual data, including revenue, cost of sales, margins and sales deductions.
This feature helps in:- Using predictive postings from sales orders, item issues and billing documents, you can assess prospective profitability before transactions take place.
- Comparing anticipated data against planned or actual data from past periods to acquire insights and detect discrepancies.
- Narrow down your search, use filters based on time periods, organizational units, customers, products and accounting attributes.
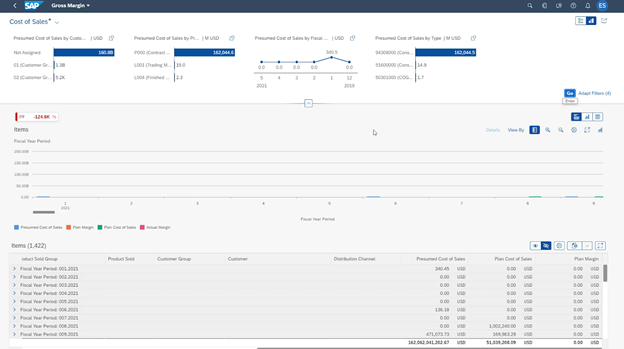
Here’s a screenshot of the dashboard of the Gross Margin – Presumed/Actual App. It tracks SAP’s cost of goods sold (COGS), which is essentially how much it costs to manufacture and sell its products. It highlights three main points:
- Current Gross Margin: 124,800.
- Cost breakdowns: See how much it costs to produce items for various clients, products and timeframes.
- In-depth analysis: It showcases that SAP S/4HANA dives deeper into 1,422 individual items or product groups
2. Granular data, insightful reports:
Avoid a one-size-fits-all approach to reports. SAP S/4HANA for profitability analysis allows you to drill down into individual cost components such as material, labour and overhead. Moreover, profitability can be analyzed by product, customer, region or any other relevant dimension. Determine which areas are driving profits and identify hidden cost drivers.
3. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) Split
With this crucial functionality in SAP S/4HANA, the specifics or breakdown of COGS are visible in accounting, which is new to the account-based COPA compared to previous versions of the SAP system. The cost of goods sold is meticulously sliced and diced according to your cost component layout.
Its benefits are–- This allows for a more in-depth study of the cost of products sold in financial accounting and margin analysis, as well as offering a differentiated view of the cost drivers to corporate management.
- This functionality improves the visibility of production variations and increases transparency by allowing for the integration of actual costing into this logic.
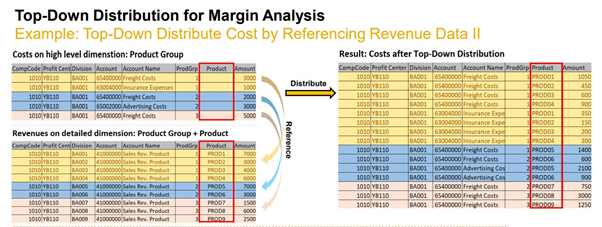
4. Top-Down Distribution
Let’s say you’re sharing rent costs in a shared residence. You may pay the total rent, but how much do your roommates contribute? Top-down distribution does the same for both costs and revenue.
This functionality in SAP S/4HANA assigns revenue and expenditures at granular levels such as the product level.
For example, as a CFO, you see overall revenue for your clothing line. Top-down distribution allocates those costs to specific products like shirts, pants and dresses based on factors like production volume or sales volume.
Thus, it also allows for more precise profitability reporting by assigning expenditures to specific revenue sources.
SAP S/4HANA’s CO-PA module is not just a reporting tool, it’s a game-changer for financial operations. Using the help of SAP S/4HANA, organizations can empower their CFOs with–
- Real-time insights
- Streamlined processes
- Data-driven decision-making capabilities
- Navigate the competitive landscape with confidence
5. Costing-Based and Account-Based CO-PA Coexistence
SAP S/4HANA allows organizations to continue using costing-based CO-PA while encouraging activation of account-based CO-PA. Its key benefit lies in the fact that this provides flexibility during the transition and allows businesses to migrate to account-based CO-PA at their own pace without losing historical data.Read more: Conquer Capacity Planning in SAP S/4HANA with VC ERP6. Mapping Variance Split
Production variances are typically classified into three categories: material price variance, quantity variance and yield variance. Previously, these categories were part of the SAP system’s Costing-based CO-PA, which limited your visibility and analysis options. Here’s a snapshot of analysing contribution margins for individual products.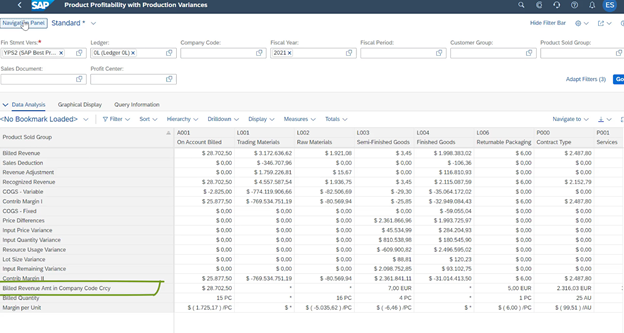
The Variance Split feature enables you to assign each variance category to a separate P&L account in SAP S/4HANA. Its benefit?
- Well, this direct mapping eliminates the need for complex reconciliations and gives you immediate insight into the financial impact of each variance.
- Thus, all data, including variance figures, is stored and updated in real-time. No more waiting for out-of-date reports to determine current production efficiency.
- In addition, granular variance insights drive targeted improvement efforts which ultimately lead to optimal resource allocation and cost-reduction strategies.
For a CFO, this kind of real-time data allows one to forecast potential variance impacts and proactively adjust production plans for improved profitability.
If you’re looking to take your financial operations to the next level, consider implementing SAP S/4HANA and leveraging its advanced CO-PA capabilities. With VC ERP Consulting as your trusted SAP S/4HANA implementation partner, you can gain expert guidance and ensure a smooth transition to this powerful ERP.
Read more: Why Business Partner Configuration is the Cornerstone of SAP S/4HANA’s Scalability
A Profitable Path Forward
SAP S/4HANA Profitability analysis has emerged as an effective tool for businesses to navigate the complexities of financial performance. As we’ve seen throughout this article, it enables decision-making through real-time insights, detailed data and insightful reports.
CO-PA shines a light on the often-muddled waters of financial analysis, tracking profit from order to receipt and anticipating potential impacts.
But the journey does not end here. SAP S/4HANA for profitability analysis continues to evolve, adding features such as Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) split and Top-Down Distribution, which expands CO-PA’s capabilities. With real-time variance insights and a smooth transition from costing-based to account-based analysis, the future of profitability measurement appears bright.This begs the question: how can you start down this path to profitability?
VC ERP Consulting, a leading SAP implementation partner, is ready to guide you. With extensive experience and a team of dedicated experts, VC ERP can assist you in leveraging CO-PA’s capabilities and realizing the full potential of SAP S/4HANA.
Investing in a strong profitability analysis solution and working with a reputable implementation partner, such as VC ERP, paves the way for a future of data-driven decision-making, optimized resource allocation and, ultimately, long-term business growth.
Contact the best SAP S/4HANA implementation partner VC ERP Consulting today to take the first step toward a more profitable future.







